Bridging the Gap in Time: Understanding and Utilizing Julian to Gregorian Calendar Converters
Related Articles: Bridging the Gap in Time: Understanding and Utilizing Julian to Gregorian Calendar Converters
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Bridging the Gap in Time: Understanding and Utilizing Julian to Gregorian Calendar Converters. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Bridging the Gap in Time: Understanding and Utilizing Julian to Gregorian Calendar Converters
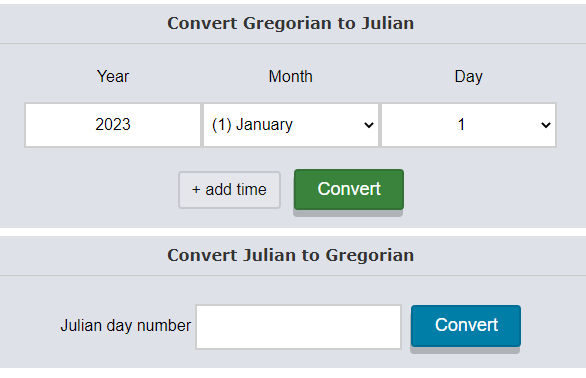
The passage of time is a constant, yet its measurement has been subject to various interpretations throughout history. Two prominent calendar systems, the Julian and Gregorian, have shaped our understanding of dates and their significance. While the Gregorian calendar is the dominant system used worldwide today, the Julian calendar remains relevant in specific contexts, particularly in historical research and religious observances. This necessitates the use of tools that bridge the gap between these two systems, allowing for accurate conversion and understanding of dates across different historical periods.
The Julian Calendar: A Legacy of Roman Influence
The Julian calendar, established in 45 BC by Julius Caesar, was a significant advancement in timekeeping. It introduced a more accurate solar year, consisting of 365.25 days, with the addition of a leap day every four years. This system remained the standard calendar across Europe and the Western world for centuries, impacting various aspects of life, from religious observances to administrative records.
The Gregorian Calendar: A Refinement for Accuracy
The Gregorian calendar, introduced in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII, aimed to correct the inaccuracies inherent in the Julian calendar. The Julian calendar, despite its leap year system, overestimated the length of the solar year by approximately 11 minutes and 14 seconds. This small discrepancy, while seemingly insignificant, accumulated over time, leading to a significant drift in the calendar’s alignment with the solar year. This drift posed challenges for accurately determining the dates of equinoxes and solstices, impacting religious observances and agricultural practices.
The Gregorian calendar addressed this issue by introducing a more precise system. It removed three leap days every four centuries, except for those divisible by 400, resulting in a more accurate representation of the solar year. This refinement, while subtle, had significant implications for the accurate dating of historical events and the synchronization of astronomical phenomena with calendar dates.
The Need for Conversion: Bridging Historical Gaps
The transition from the Julian to the Gregorian calendar was not immediate. Different regions adopted the Gregorian calendar at varying times, leading to discrepancies in date recording. This necessitates the use of conversion tools to accurately translate dates between the two systems. A Julian to Gregorian calendar converter plays a crucial role in bridging this historical gap, enabling researchers, historians, and individuals to understand and interpret dates across different time periods.
Understanding the Conversion Process: More Than Just Adding Days
The conversion from Julian to Gregorian dates is not simply a matter of adding or subtracting days. The difference between the two calendars is not constant, but rather grows over time due to the varying leap year rules. A Julian to Gregorian converter takes into account these nuances, calculating the precise difference between the two systems based on the specific date being converted.
Beyond Dates: Applications in History, Religion, and Astronomy
The ability to convert dates between the Julian and Gregorian calendars has significant applications in various fields:
- Historical Research: Historians rely on accurate date conversions to understand the chronology of events, analyze historical records, and interpret historical narratives. Understanding the date system used in historical documents is crucial for accurate historical analysis.
- Religious Observances: Many religious traditions, particularly those with historical roots in the Julian calendar, continue to follow its system for determining religious holidays and festivals. Conversion tools are essential for understanding the dates of these observances in the context of the Gregorian calendar.
- Astronomy: Astronomical events, such as solstices and equinoxes, are tied to the solar year and are often referenced using dates based on the Julian calendar. Converting these dates to the Gregorian system allows for a more accurate understanding of their occurrence in relation to modern calendar systems.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: When did the Gregorian calendar become the standard?
A: The Gregorian calendar was adopted by different countries at various times. While it was introduced in 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII, its widespread adoption occurred gradually throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, it is the dominant calendar system used worldwide.
Q: How do I know which calendar a historical document is using?
A: Determining the calendar system used in historical documents requires careful analysis. Contextual clues, such as the region where the document originated, the time period it covers, and the specific historical events it describes, can provide insights into the calendar system used.
Q: Are there any differences between the Julian and Gregorian calendars besides the leap year rules?
A: Yes, there are some minor differences in the numbering of days and months between the two calendars. For example, the Julian calendar has a different day-of-week correspondence with the Gregorian calendar.
Q: Is it possible to convert dates from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar for dates before 1582?
A: Yes, it is possible to convert dates from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar for dates before 1582. However, the conversion becomes more complex for dates further back in time due to the increasing difference between the two calendars.
Tips for Effective Use of Julian to Gregorian Converters
- Choose a reliable converter: Ensure that the converter you use is accurate and up-to-date, taking into account the nuances of the conversion process.
- Double-check your inputs: Carefully verify the date you are converting, ensuring that the year, month, and day are accurate.
- Understand the context: Consider the historical context of the date you are converting, as this can provide valuable insights into the calendar system used.
- Consult with experts: If you are unsure about the conversion process or have specific questions, consult with historians or experts in calendar systems.
Conclusion: Bridging the Past and Present
Julian to Gregorian calendar converters are essential tools for bridging the gap between historical and modern timekeeping. These converters allow for accurate translation of dates between these two systems, facilitating historical research, religious observances, and astronomical studies. Understanding the complexities of these two calendar systems and the nuances of their conversion is crucial for accurate interpretation of historical events and the understanding of time across different cultures and periods. As we navigate the complexities of history and the diverse ways in which time has been measured, these tools provide a valuable bridge between the past and present.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Bridging the Gap in Time: Understanding and Utilizing Julian to Gregorian Calendar Converters. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!